A subtle loss: visual and anatomic changes in HIV retinopathy
New technology is allowing clinicians, for the first time, to study the subtle structural changes that cause progression of this disease.
Diagnosing HIV retinopathy
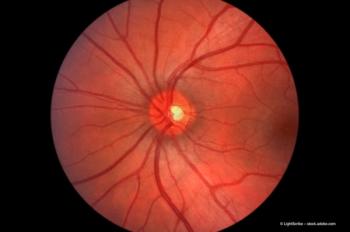
HIV retinopathy is an ischaemic microangiopathy that leads to damage of inner retinal structures including the vasculature and ganglion cells. Clinically, HIV retinopathy is diagnosed by the presence of intra-retinal haemorrhages and soft retinal exudates (cotton wool spots) in patients with low CD4 T-lymphocyte cell counts (<100 or 1.0 x 109/L) in the absence of infectious retinitis. Upon a patient's immune recovery, HIV retinopathy usually resolves within three months. However, if a patient's immune status is not recovered, these signs may persist or worsen while the CD4 cell count remains low.
OCT allows imaging of subtle changes
The advent of more sophisticated retinal imaging technology has opened up new possibilities for studying structural changes in HIV retinopathy. Many of these instruments are already in clinical use for glaucoma and other retinal diseases.
One hypothesis to explain vision loss is that it may be caused by permanent infarctions of the retinal nerve fibre layer from previously resolved cotton wool spots, areas of retinal capillary dropout, or both. Using OCT, we have been able to demonstrate visible inner retinal structural changes long after cotton wool spots have disappeared on ophthalmoscopic examinations. The inner retinal tissue in the area of cotton wool spots remains more dense than adjacent retina (hyper-reflective sign), which may mean chronic oedema or glial transformation of the tissue. It may be that such a cumulative damage from multiple infarctions and haemorrhages can finally lead to changes in the nerve fibre layer of the retina. Fortunately, the progress in technology now means we have the advantage of detecting some of these changes in vivo.
Newsletter
Get the essential updates shaping the future of pharma manufacturing and compliance—subscribe today to Pharmaceutical Technology and never miss a breakthrough.