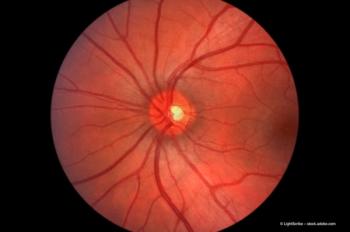
Expanding our knowledge of dry AMD
Professor Scott Cousins explains how we can use our knowledge of drusen formation to find new ways to combat dry age-related macular degeneration.
Key Points
Drusen development: the four theories
Currently, there are four key theories for explaining drusen formation. These are:
The role of inflammation
Our understanding of the disease has evolved rapidly in recent years. "I think that the greatest breakthrough in understanding the pathogenesis of drusen that we have had in the last five to seven years is this idea that inflammation, in various forms, is a major contributor to the disease; that the innate immune system plays a major role," asserted Professor Cousins. "In the last three years, there has been a lot of data published that show that the genetic impetus of AMD is found among the complement inhibitors in the complement system; specifically, Complement Factor H is the most important susceptibility gene.
"My laboratory, among others, has also looked at the role of one of the circulating white cells: the monocyte. We already know that its tissue equivalent, the macrophage, has a major role to play in wet AMD, but we're now learning it plays a role in dry AMD as well, and so we're exploring what this may mean for the development of the disease," Professor Cousins explained.
"The most recent breakthrough in our understanding was published in a New England Journal of Medicine article,"1 Professor Cousins continued. As previously reported by Ophthalmology Times Europe,2 this study examined the role of a mutation of the toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) gene. TLR3 is a protein that alerts the immune system to infections, and a mutated form of the TLR3 gene, expressing leucine instead of phenylalanine, was shown to be protective against geographic atrophy, most likely by suppressing the death of RPE cells.
Newsletter
Get the essential updates shaping the future of pharma manufacturing and compliance—subscribe today to Pharmaceutical Technology and never miss a breakthrough.